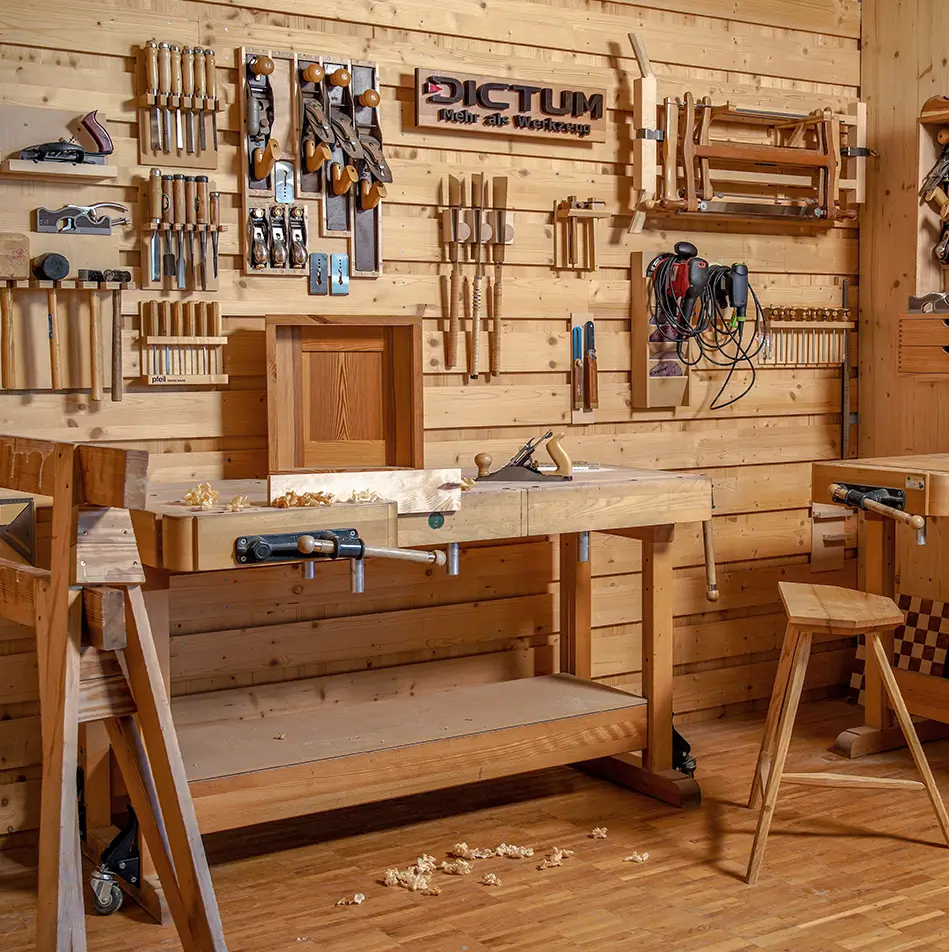
Soil cultivation
Soil cultivation
EXPERTENWISSEN ABZIEHLEDER
What Tools are available for soil cultivation?
Hoes & claws. They are part of the basic equipment of garden tools. A basic distinction is made here between one-handed and two-handed tools. The range of applications is quite broad. Claws are mainly used to loosen the soil. This ensures better aeration and nutrient absorption. A cultivator or sow tooth, for example, is suitable for this. This is also available for precise loosening between flowers, as a one-handed sow tooth. We also have the right hoes for sickling, weeding and cultivating lawns.
Shovels & planting trowels. Planting shovels and planting trowels differ minimally. Both tools are used to plant young plants in your bed and for general gardening work. The difference lies in the end of the tool. The planting trowel has a pointed end, while the shovel has a rounded end.
Tip: It is recommended that aerification is carried out once a year with a spacing of approx. 12-14 cm, i.e. approx. 50-60 holes per m2. After aerification, sand should be filled into the holes.
Spades. The shovel is often confused with or called a Spades. However, the Spades is a special form of shovel. It is mainly used to pick up material on the shovel blade and transport it to another location. Spades are specially designed for digging in agriculture. Digging forks with long steel tines are also used for digging.
Planting knife. These small knives are used for repotting plants. The hollow back makes this possible. These knives usually have a serrated side. This makes it possible to remove smaller roots.
Rake. Probably the best-known garden tool is the rake. It is used to remove leaves and undergrowth. There is a special type of scarifying rake that can be used to remove moss and lawn thatch from small areas.
What types of soil are there?
When working the soil and maintaining the lawn, it is important to differentiate between soil types. Broadly speaking, a distinction is made between dry and moist soil. A distinction is also made between light, medium and heavy soil. A light soil has a high sand content and is therefore easy to work and prevents waterlogging. The disadvantage of sandy soil is its low water storage capacity and low nutrient content.
The medium soil type is silty soil. This is favoured by many, as this soil provides an optimal basis for sowing most plants. A silty soil has a balanced ratio of air and water, which enables a high storage capacity of water and nutrients. If the soil is too silty, sand must be added.
A heavy soil contains a lot of clay. Although this has a large storage capacity for water and nutrients, there is a risk of acidification, poor aeration and moss formation. Sand and organic material such as humus or bark mulch must therefore be added to clay soils.